Acetylpyridine: Common isomers, applications, storage and toxicity
Acetylpyridine is an odorless and tasteless compound having the chemical formula C7H7NO and exists in its natural state as a liquid. It is a pyridine derivative that has an acetyl group attached to the ring structure of the pyridine molecule. According to the chemical formula of acetylpyridine, its molecular weight is 121.14 g/mol.
There are three main isomeric forms of acetylpyridine:
- 2-Acetylpyridine
- 3-Acetylpyridine
- 4-Acetylpyridine
All of these isomeric forms can be discussed in detail as following:
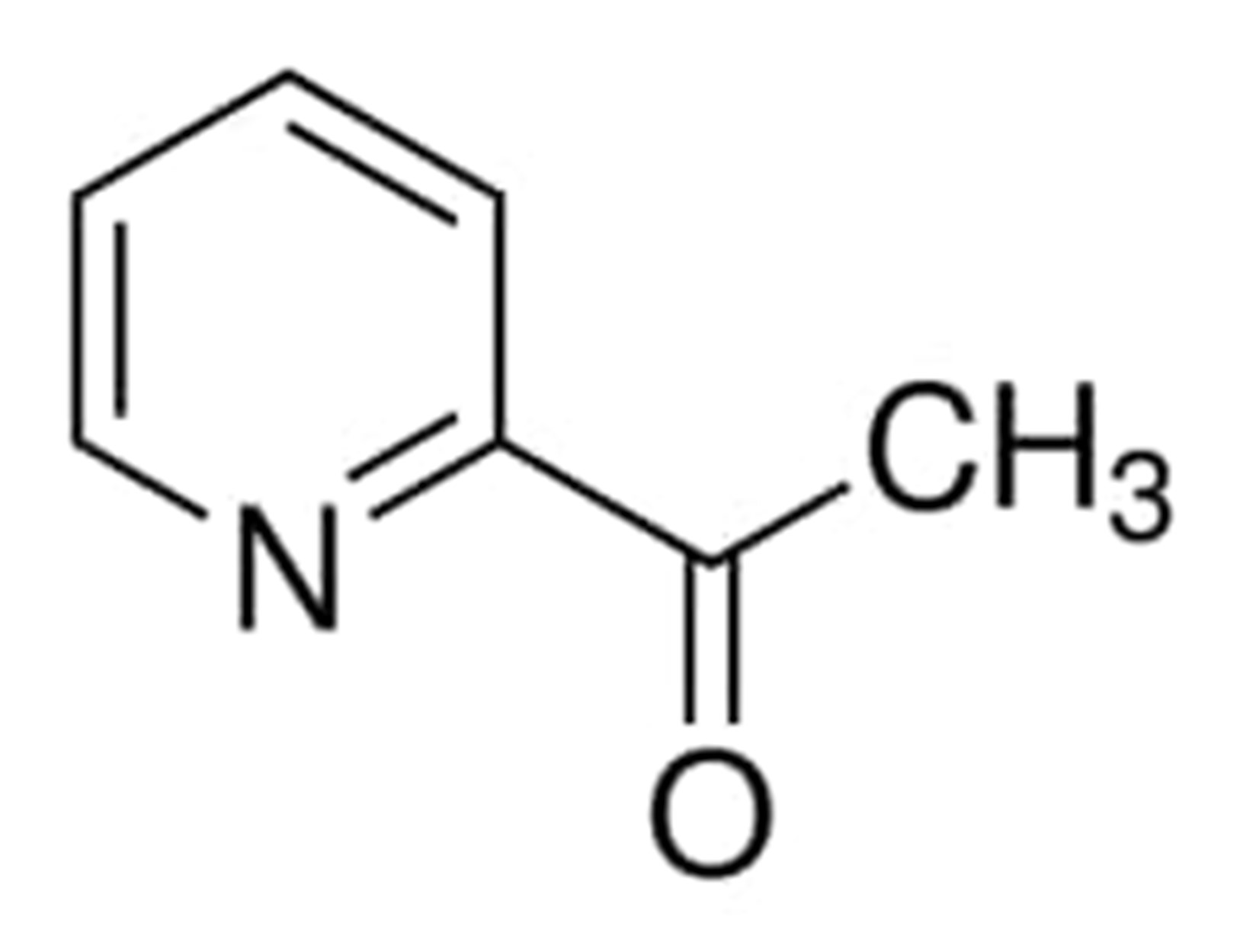
2-Acetylpyridine
2-Acetylpyridine is the common name for the organic compound that may be represented by the formula CH3COC5H4N. It is a typically used as a flavoring agent and is a colorless liquid with a thick consistency. 2-acetylpyridine is naturally present in Mentha arvensis, Phaseolus vulgaris, and Camellia sinensis.
It is a liquid that can be clear or a light yellow in color, and it has a strong, fatty, and savory aroma that conjures up images of tobacco and popcorn. The color range of this liquid is clear to light yellow.
This compound has a molar mass of 121,139 grammes per mole. It is possible to dissolve it in acids and ether, and the temperature at which it boils is 192.0 degrees Celsius. It is also known by the names such as Methyl 2-pyridyl ketone, 2-ACETYLPYRIDINE, 1122-62-9, 1-pyridin-2-ylethanone, and 1-pyridin-2-ylethanone.
The chemical structure of 2-Acetylpyridine can be written as:
Uses
- The principal application for it is as an addition to several other flavors. In addition to occurring naturally in malt, it is produced by the Maillard reaction and the nixtamalization process. Corn's flavoring capabilities are put to good use in a variety of foods and beverages, including tortillas, popcorn, and beer.
- It has the potential to be utilized in the production of a near-infrared fluorescence probe, which has the capability of monitoring pH levels in living cells in real time.
- Biologically active ligands that have the potential to be included into the formation of complexes containing metal ions such as Co(II), Ni(II), Cu(II), and Zn(II) (II).
- It is a luminescence probe that is capable of detecting singlet oxygen and is triggered into action by a certain period of time.
- Both a potent antiproliferative drug and iron chelator, 2-aminopyridine thiosemicarbazones are a kind of pyridine derivative.
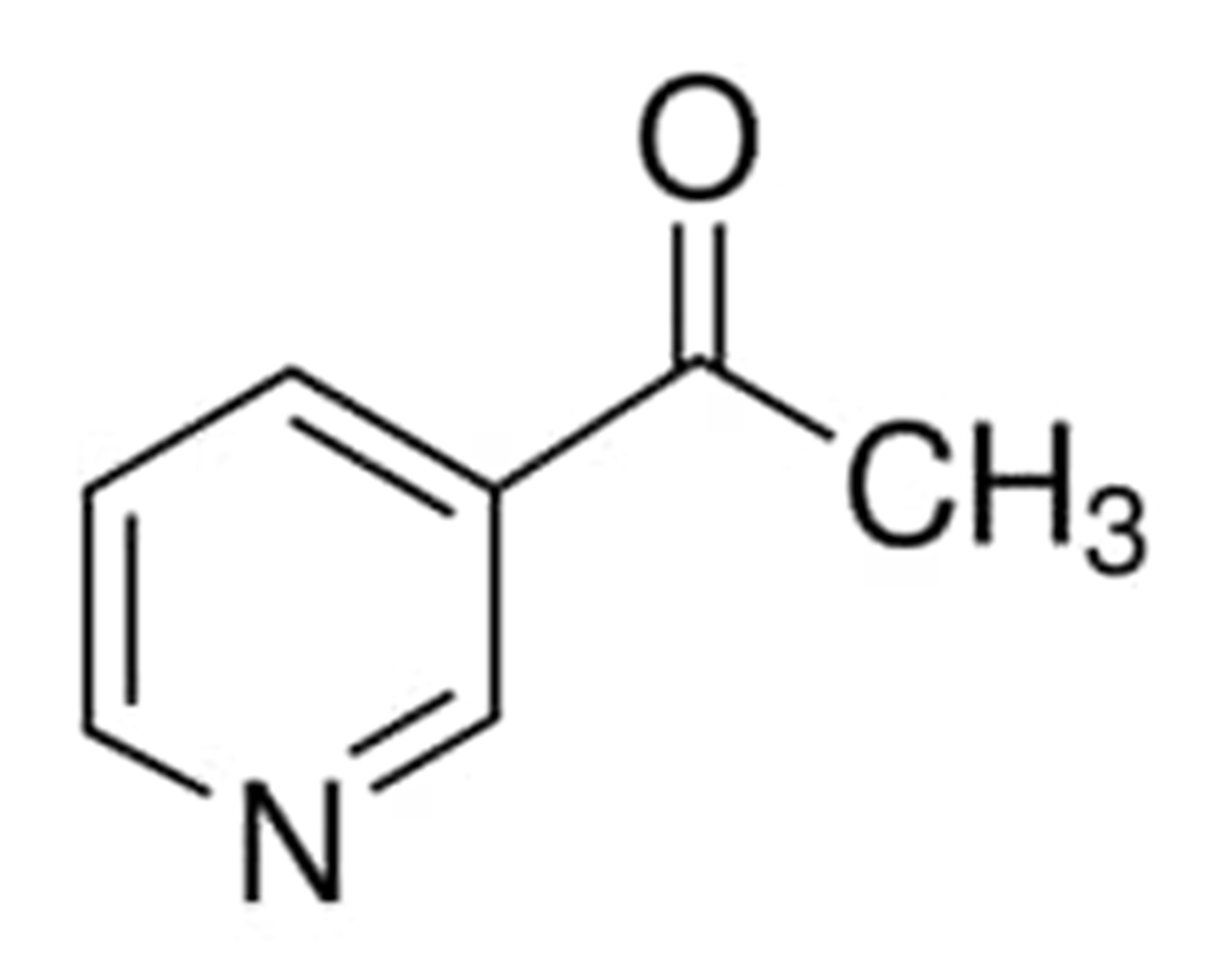
3-acetylpyridine
3-Acetylpyridine is a liquid that can range in color from colorless to yellow with a sweet, nutty, and popcorn like aroma. It is sometimes referred to as 1-(pyridin3yl) ethanone, 1-pyridin-3-ylethanone, and 3-Acetopyridine. It is a chemical compound that has the chemical formula C7H7NO. It melts at temperatures of around 11-13 degrees Celsius and boils at temperatures of 220 degrees Celsius (lit).
The chemical structure of this compound can be written as:
Uses
- This compound is used as a flavoring agent.
- In baked goods, it is added at concentrations of 3 parts per million, while in sweets and beverages, it is used at concentrations of 2 parts per million, in order to mimic the flavors of popcorn, peanuts, pork, and tobacco.
- In addition, the creation of the bone resorption inhibitor known as risedronate sodium requires this process in order to be completed. Additionally, it is an essential component in the production of scented candles and fragrances.
Storage
Keep containers well sealed and store them in a cool, dry place having enough light and the storage space should be wide open. Maintain a safe distance from any and all sources of oxidation.
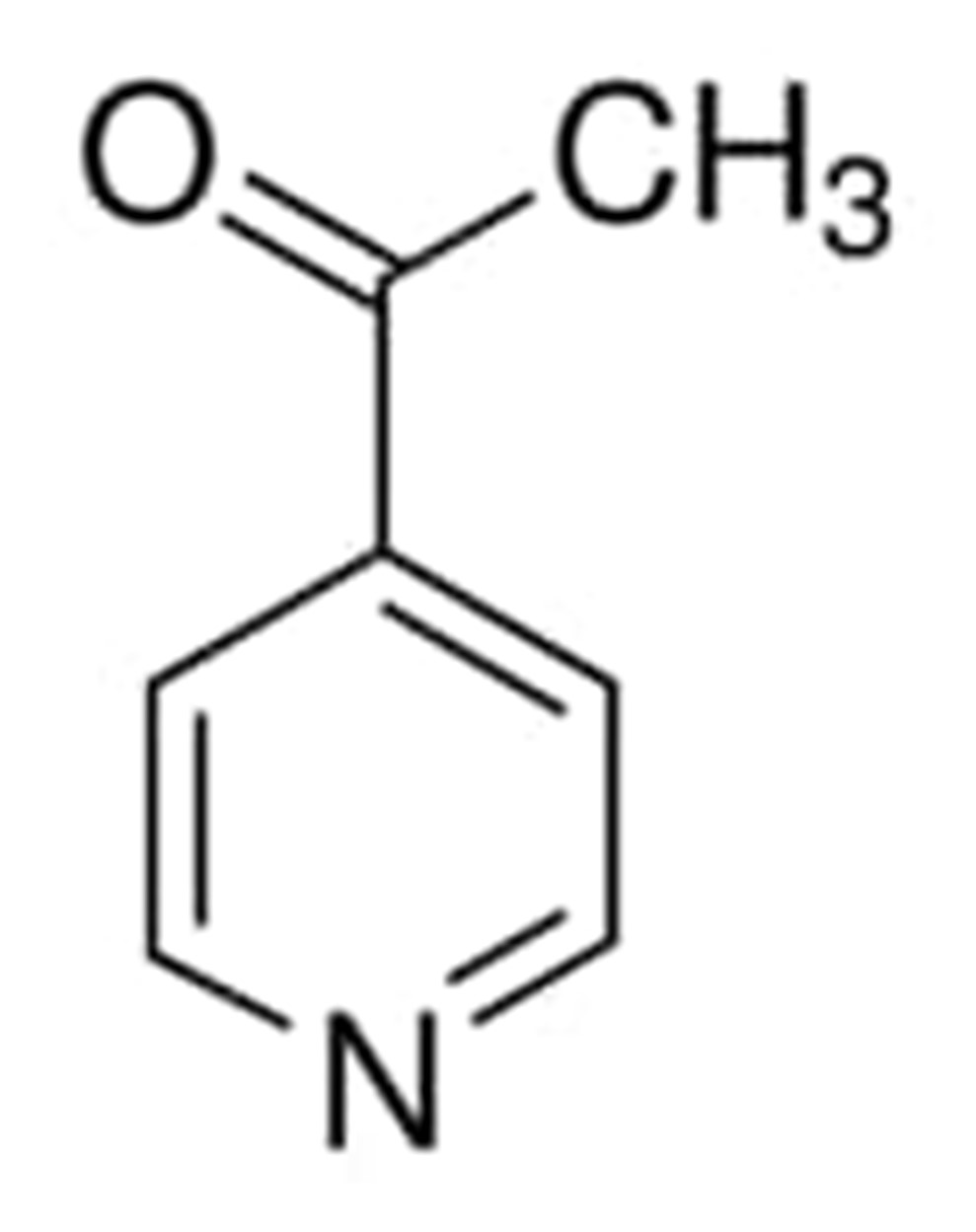
4-Acetylpyridine
4-acetylpyridine in its liquid form has a hue that is comparable to that of a dark amber. It has a point of melting at 16 degrees Celsius and a point of boiling at 414 degrees Fahrenheit at 760 millimeters of mercury. This material will dissolve at a concentration of 100 mg/mL or higher when the temperature is 66 degrees Fahrenheit.
This compound is also used as a flavor enhancer.
The chemical structure of this compound can be written as:
Toxicity
Because it is an irritant, this material can aggravate irritation in the upper respiratory tract, the skin, the eyes, and the mucous membranes if it comes into contact with them. This material may be harmful if it is consumed, breathed in, or absorbed via the skin. It irritates the eyes, nose, and respiratory tract, causing discomfort in all three. Toxic carbon monoxide, carbon dioxide, and nitrogen oxide gases are emitted during decomposition.