Applications of Chloropicolinic acid
Picolinic acid as anti-bacterial
Picolinic acid has been shown to have a variety of possible impacts on the body when used alone in experimental settings, notably in regards to immune function and antibacterial activity.
Expression of the macrophage inflammatory proteins (MIP)
It has been shown in vitro that picolinic acid (PIC) (at supernatant concentrations of 1-4 mM) can increase interferon- (INF)-dependent nitric oxide synthase (NOS) gene expression and promote expression of the macrophage inflammatory proteins (MIP), hence boosting macrophage effector activities. PIC-mediated induction of MIP and is assumed to occur via an iron chelation dependent pathway; however the mechanism creating the synergism with IFN- is unknown. Selective inhibition of HIV, HSV, and SV has been documented at high PIC doses (1-4 mM) in culture.
Picolinic acid as antiviral
PIC's antiviral activity appears to originate from its cytotoxic effect, which leads to an increase in death of infected cells and a decrease in viral multiplication. Combining PIC and IFN has also been found to suppress J2 retrovirus expression, albeit the mechanism by which this occurs is unclear.
Anti-microbial activity against Mycobacterium aviumcomplex (MAC)
Mycobacterium aviumcomplex (MAC) has been shown to be susceptible to PIC's (2.5-40 mM) antimicrobial activities, and PIC has been shown to significantly augment the antimicrobial activity of the medicines clarithromycin, rifampin, and different fluoroquinolones. One possible explanation for PA's antimicrobial effect against MAC species is that it is able to chelate metal ions, including Fe2+ and Zn2+, which are required for microbial survival.
Anti-tumor activity of Picolinic acid
PIC has been shown to inhibit tumor development by a subset of researchers. Mice injected with MBL-2 lymphoma cells lived much longer than controls after receiving PIC (100 mg/Kg) injections in conjunction with activated macrophages, as shown by in vivo investigations. It has been hypothesized that IFN- mediates these effects by stimulating macrophages to take action.
Picolinic acid as an anti-infective and immunomodulator
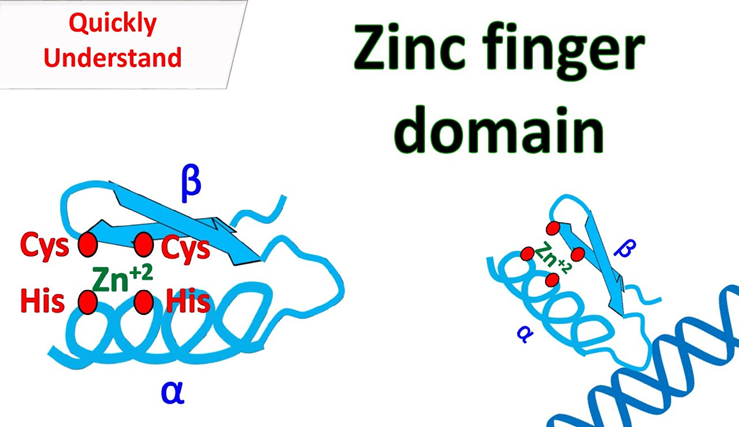
PCL-016, also known as picolinic acid drug substance, is a metabolite of tryptophan that consists of a pyridine carboxylate. It is synthesized by the body between 25 and 50 milligrammes per day from the breakdown of tryptophan and functions as an anti-infective and immunomodulator. To put it simply, PCL-016 is essential for zinc transfer. The chemical is effective as a therapeutic drug because it binds to zinc finger proteins (ZFPs), modifying their structures and interfering with zinc binding to prevent them from functioning. ZFPs have roles in both the homeostatic regulation of cells and the replication and packaging of viruses. The antiviral effects of picolinic acid have been demonstrated in both in vitro and in vivo, and it has been found to occasionally act in tandem with other cytokines, like interferon gamma, to influence immune responses. PCL-016 has the potential to treat viral diseases such acne vulgaris, herpes, and others.
Chromium picolinate in insulin resistance
As an established dietary supplement, chromium picolinate is used to treat insulin resistance.
Picolinic acid role in Central Nervous System
Effects on the central nervous system have been called into question, and this complex has been called into question as to why. Divalent metal complexes of PIC are not easily transported through lipid bilayers, according to the research of Aggett et al.69. The poor solubility of PIC in a lipophilic liquid is reflected in its low partition coefficient (logP = 0.098a). It's therefore quite improbable that PIC would independently breach the BBB. Additionally, Smythe et al.8 found that PIC plasma levels were at values that were 3-15 times greater than those in the brain tissue and CSF (Table 2). It is hypothesized that a little amount of PIC can flow from the central nervous system to the rest of the body while still allowing for the maintenance of the concentration ratio.
Chromium-picolinate role in metabolic syndrome's
In terms of metabolic syndrome's secondary complications, nephropathy ranks as the most common. Chromium-picolinate, a nutritional supplement, is thought to have renoprotective properties. However, worries regarding chromium-safety picolinate's have been amplified by reports of potential harmful consequences. The study's design was to test whether or whether DNA damage and widespread modifications in core detoxification / cell-cycle regulating pathways occur during treatment with clinically relevant dosages of chromium-picolinate, a drug used to treat diabetes. Both the participants and the researchers remained anonymous during the whole trial. The db/db mouse model was employed with clinically appropriate dosages of chromium-picolinate. DNA breakage was measured using the Comet Assay as an indicator of DNA damage. In order to gain insight into the central detoxification and cell-cycle regulating mechanisms under the treatment settings, the expression patterns of SOD-1 and P53 were analyzed on an individual and group level. The results of the experiments showed a very individual response to the different types of therapy. For the most part, DNA-damage variability was shown to be greatest after long-term therapy with high CrPic dose. Treatment with chromium-picolinate was shown to decrease expression in a dose-dependent manner, as evidenced by the subcellular imaging and expression patterns. READING AND SUGGESTIONS: The number of people who might get diabetes is staggering, and it's becoming a global epidemic. Possible contributing factors include previous unsuccessful attempts to avoid the disease through the use of synthetic supplements and medications whose particular hazards are rarely recognized. Therefore, it is preferable to use a comprehensive, integrated approach to healthcare that includes predictive diagnostics, targeted prevention, and individualized treatment algorithms.
Picolinic acid as a feed for rats
Picolinic acid supplemented meals caused considerably greater weight growth in rats than unsupplemented diets, whether the food was based on soybean protein or casein. Kidney zinc concentrations of rats administered picolinic acid-supplemented meals were much higher than those of rats fed control diets. Compared to rats fed a pyridoxine-deficient diet that was not supplemented with picolinic acid, rats fed a pyridoxine-free diet that was prepared with vitamin-free casein acquired much more weight. In comparison to rats fed a pyridoxine-deficient diet without picolinic acid supplementation, rats fed the supplemented food had a considerably higher zinc content in their kidneys. Rats supplemented with picolinic acid had better dietary zinc absorption and food efficiency. It appears that picolinic acid may improve the bioavailability of dietary zinc and maybe other divalent cations.