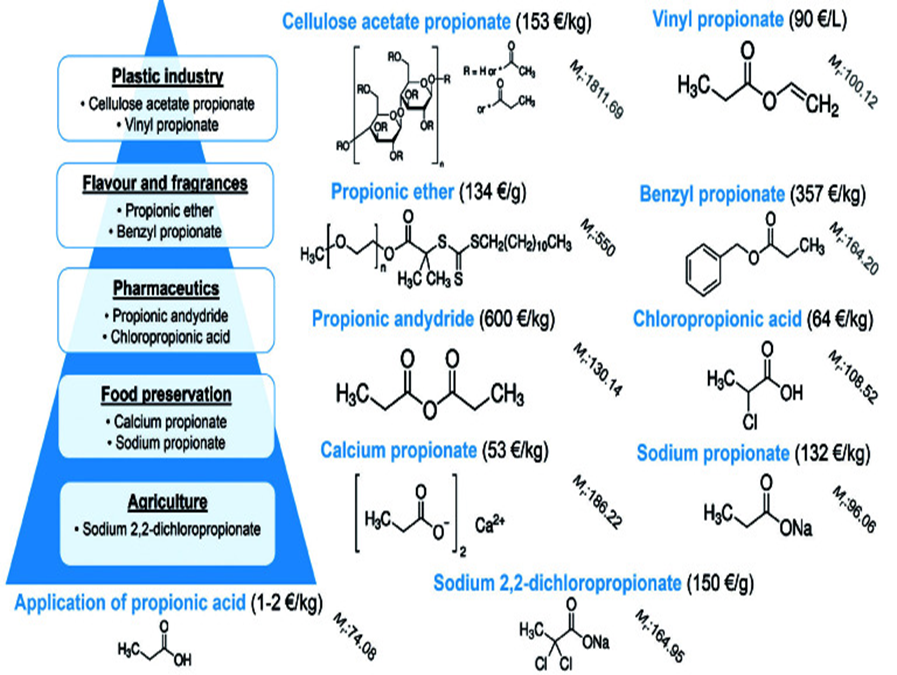
Applications of Propionic Acid
Propionic acid as an intermediate
There are several chemical reactions where propionic acid can serve as an intermediate. The substance can be utilized to alter man-made cellulose fibers. It's found in certain medications and herbicides. Propionic acid esters have found applications as solvents and synthetic flavorings.
Propionic acid as antibacterial agent
The sodium salt of propionic acid, sodium propionate, is a clear, colorless, or almost colorless crystalline powder or granular solid. As an antibacterial agent for food preservation and taste, it is a food additive that the FDA has deemed generally recognized as safe (GRAS). As a food additive, it has also been given the green light in Europe. To make sodium propionate, just mix some sodium hydroxide with propionic acid to neutralize it. Sodium propionate, the main component of Amino-Cerv, has been officially recognized as a safe and effective medication in Canada (used to treat inflammation or injury of the cervix).
Propionic acid as antimicrobial
Many different types of microbes are capable of fermenting glucose into propionic acid, and many others can metabolize it. By building up in the cells, impeding metabolic routes, and inhibiting enzymes, PA has an inhibitory impact on the bacteria that metabolize it. There is a dose-dependent decrease in intracellular pH caused by PA, which, together with an increase in intracellular anions, limits microbial growth.
As a moderately powerful organic acid, propionic acid has been used as an antibacterial agent in the preservation of foods including dairy and baked items, as well as animal feed. Feed can be protected from bacterial and fungal deterioration by treating it with PA instead of antibiotics, which could lead to antibiotic resistance. Many chicken feed formulations contain PA to lessen Salmonella spp. infection and prevent undesirable mould development. PA in feed has been proven to increase ruminal productivity by accelerating substrate decomposition (by 8%) and decreasing methane generation (by 20%), in addition to having antibacterial effects. PA, in contrast to acetate, inhibits the hydrocarbon to methane conversion. A higher concentration of lactic acid and water-soluble carbohydrates in the rumen is achieved by the use of lactic acid bacteria (LAB), which improves PA production.
Propionic acid as food preservative
Many different types of packaged goods employ propionic acid as a preservative and flavoring additive. Hay, corn, oats, wheat, sorghum, and barley are some of the animal feeds that benefit from its preservation properties. In addition to having antibacterial qualities, it inhibits the growth of a wide variety of moulds, which is why it finds usage as a preservative.
Additive for food preservation and safety
The incorporation of preservatives into food is crucial since they tend to avoid the probable spoiling that might lead to food poisoning in light of the unreliable nature of physical factors like heat, excessive wetness, unpredictable rainfall, and inadequate drying conditions.
Salts of propionic acid, such as calcium, potassium, and sodium, are frequently employed in the food industry as preservatives. Fungi are a common cause of quality and economic losses in wheat, especially when they infect wheat from other fields following harvest or when stored improperly. The application of PA and its salts during crop storage has the potential to completely eradicate these contaminations. Foods preserved using propionic acid are considered GRAS, or generally recognized as safe.
Propionic acid as disinfectant
Propionic acid can be used to disinfect the outside of silage and grain storage areas in agricultural and animal operations for the same reasons. Put some in the water that your chickens or cattle drink, and it will serve as a natural antibacterial. Relatedly, it is sprayed into poultry litter to eliminate the fungus and bacteria that might cause disease in chickens.
Propionic acid as animal feed
It has been shown that propionic acid can prevent the spread of mould and some types of bacteria. Because of this, much of the propionic acid manufactured is utilized as a preservative in food for both humans and animals, including Ballistics Gel. It can be utilized either as a pure substance or as the ammonium salt for animal feed. It is used as either sodium or calcium salt in many types of human food, but mainly in baked products. Some of the earliest anti-fungal foot powders made use of a similar formulation.
Propionic acid as anti-inflammatory
The search for highly effective new anti-inflammatory medicines has been gaining momentum during the past century. For this aim, many different organic acids have been tried, but only those that are both nitrogen-free and non-steroidal have been widely accepted as effective agents. Since the most prevalent form of propionic acid (C3H6O2) lacks nitrogen, it is frequently employed in the manufacturing of anti-inflammatory drugs.
PA's anti-inflammatory properties might be improved by adding a variety of chemical groups. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are commonly given to treat inflammatory illnesses such arthritis and rheumatism. PA with an aryl group (profens, or 2-arylpropionic acid derivatives) is a key component of these drugs.
New compounds have been proposed recently as potential auxiliary agents with PA. Patients should be aware that some anti-inflammatory medicines based on propionic acid may have stomach ulcerogenic effects. This stomach upset can be avoided by using 2-2-fluoro-4-(2-oxocyclopentyl) methyl] phenyl propionic acid in the formulation.
Propionic acid as Herbicide
When compared to other synthetic herbicides, propionic acid poses no risk to the environment since it breaks down into harmless substances like acetic and formic acids, then carbon dioxide and water. Compared to formic acid, another frequent herbicide, it is less caustic and corrosive. PA has no health risks during application if the correct formulation is applied and respiratory protection is worn. As a pre-emergent and post-emergent herbicide, propionic acid is effective against both monocotyledonous and dicotyledonous plants.
Different microbial species
Different microbial species have varying degrees of success digesting herbicides; one example is mecoprop ((RS)-2-(4-chloro-2-methylphenoxy) propionic acid), which comes in both enantiomerically pure and racemic forms. Previous research suggested that the efficiency of propionic acid-based herbicides is enhanced by using a specific formulation, since this reduces mecoprop breakdown by these organisms. However, once herbicides have been used, they must be taken out of the area where they were used since they might be harmful to people. Many different kinds of microorganisms might be employed effectively to get rid of these pathogens.