Bromopyridine: Common isomorphs, synthesis, applications and storage
Different methods exist for brominating pyridines (bromine in aqueous solution, acetic acid in oleum, bromine monofluoride, dioxane dibromide, bromine and Lewis acids, sodium hypobromite, and hypobromous acid in aqueous perchloric acid).
The chemical formula for bromopyridine is C5H4BrN, and its molecular weight is 158.00 g/mol. Bromopyridines have a boiling point of 173.0 degrees Celsius, a flash point of 51 degrees Celsius, and a vapour pressure of 1.75 millimetres of mercury. The CAS number for this chemical is 626-55-1.
Pure 3-bromopyridine may be produced by heating pyridine (4 moles) to 130°C in fuming sulphuric acid with bromine, according to the equation (1 mole). 2 C5H5N + 2 SO3 + Br2 → 2 C5H4BrN + SO2 + H2SO4
Synthesis
Pyridines may be brominated in a number of different methods, each of which can result in the production of either 3- or 5-bromopyridines. It has been shown to be difficult to achieve strict monobromination of pyridines that include strong activating groups. The bromination of pyridine or other pyridine derivatives with low activation levels, such as picolines, can only take place under forced conditions. Blocking bromination at the 3- and 5-positions makes it possible to accomplish the 2- and 6-bromination reactions. The bromination process is simplified by using a complex or an electrophile with a higher strength. The production of bromine monofluoride is accomplished by passing fluorine through a cold solution of bromine that has been dissolved in trichlorofluoromethane. This procedure is necessary for the bromination of pyridine.
There are three stable isotopes of Bromopyridine which are as following:
- 2-Bromopyridine
- 3-Bromopyridine
- 4-bromopyridine
These isotopes of Bromopyridine can be discussed in detail as following:
2-Bromopyridine
It has the chemical formula BrC5H4N and is an organic molecule. Chemically, it is a colourless liquid that serves as an intermediary in the production of organic compounds. Diazotization followed by bromination can be used to make it from 2-aminopyridine.
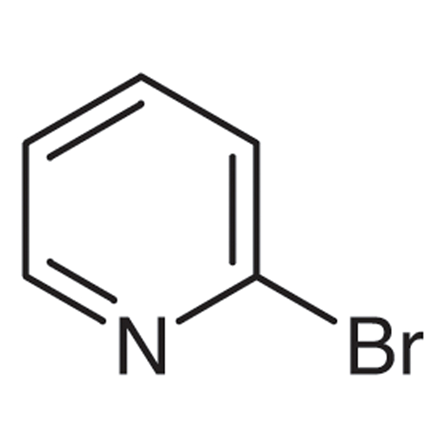
2-Bromopyridine possesses a characteristic order and its boiling point is between the range of 192°C to 194°C and its flash point is 97°C (207°F). If we talk about its solubility then it is slightly miscible with water.
Reactions of 2-Bromopyridine
The combination of butyllithium and 2-bromopyridine results in the formation of the valuable reagent 2-lithiopyridine. In a two-step process, the thiol functional group can be introduced to 2-bromopyridine by first oxidising it to the N-oxide with an appropriate peracid, then replacing the N-oxide with sodium dithionite or sodium sulphide with sodium hydroxide. This process is called the oxidative addition of the thiol functional group.
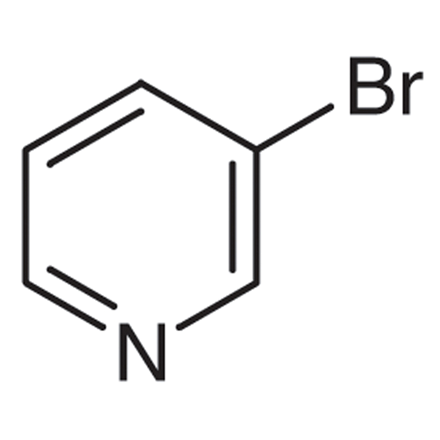
3-Bromopyridine
The chemical formula for 3-bromopyridine is C5H4BrN, and it is classified as an organohalide. Its molecular weight is 158.00 g/mol. It is a colourless liquid that is used almost exclusively in the synthesis of organic compounds during the process of chemical synthesis. In some processes, such as the Heck reaction and the Buchwald-Hartwig coupling, it acts as a substrate.
The following diagram shows the chemical structure of 3-bromopyridine:
Synthesis
It may be manufactured from 2-aminopyridine by the processes of diazotization and bromination respectively.
The following examples illustrate these brominations in their many forms:
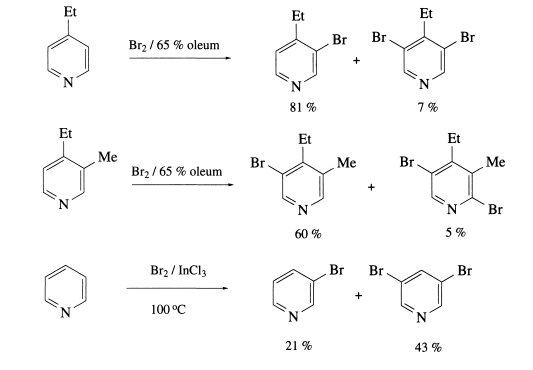
Storage
3-bromopyridine is light sensitive and air sensitive compound so must be stored in an air tight amber colored glass bottle under inert gas.
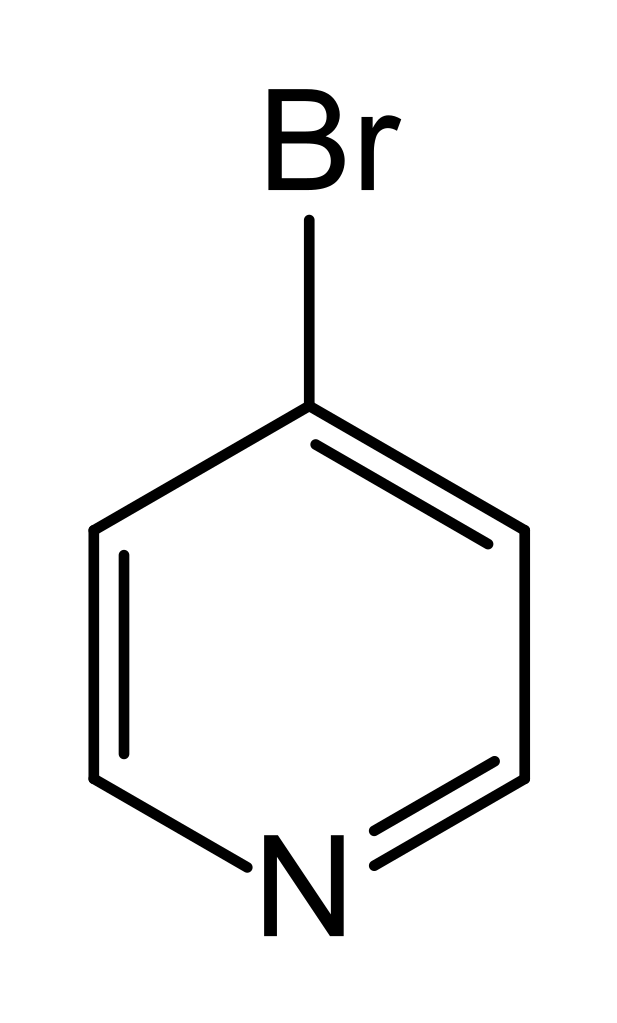
4-Bromopyridine
4-bromopyridine is an organic solid with the molecular formula C5H4BrN and molecular weight 194.46 g/mol. It is soluble in DMSO, Methanol and Water
The chemical structure of 4-bromopyridine is as following:
Storage
It is hygroscopic in nature so must be stored with caution.
Place in a freezer at -20 degrees. Moisture, strong bases, and powerful oxidising agents are examples of materials that are not compatible with it. Protect from humidity and air and store Under Inert Gas
Synthesis of Bromopyridines
Selective monobromination has proven difficult for pyridines with strong activating groups. For example, pyridine and picolines cannot be bromated unless specific conditions are satisfied. By preventing bromination at the three- and five-positions, two- and six-bromination can be achieved. Using complexed pyridine or a more powerful electrophile, bromination can be more readily accomplished. Bromine monofluoride is generated in situ when fluorine is passed through a trichlorofluoromethyl solution of bromine. Pyridine can be bromined with this chemical.
A strong activating group, such as hydroxy or amino, makes bromination simpler if the ortho and para bromination sites are unblocked. Monobromation of 3-hydroxypyridines in alkaline aqueous solutions is common. You get a dibrominated product by increasing the bromine content of the substrate. At the conditions studied, only a few mono 4- bromo compounds could be identified.
Uses of Bromopyridines
Compounds such as 2-acetylpyridine, fluorenone, pyritione, aminopyridine, azacyclonol and chloropyramine are some examples of the kinds of chemical substances that may be produced with the help of bromopyridine.
The chemical 2-Bromopyridine can be used in the production of bioactive compounds like antimalarial medicines. Additionally, the use of it is required in order to produce beta-adrenoceptor agonists.
Applications of 4-Bromopyridine may be found in the pharmaceutical sector. These applications include the commercialization and ongoing manufacture of abiraterone.