Cyanopyridine: Common isomorphs, applications, side effects and safety
Cyanopyridines is the cyanide derivatives of pyridine. Its molecular formula is C6H4N2 and carries the molecular weight of 104.11g/mol. In the processes that involve formation of C–C bonds and transition metals, cyanopyridines are excellent coupling partners. There are three main isomeric forms exist of cyanopyridine which are as following:
- 2-Cyanopyridine
- 3-Cyanopyridine
- 4-Cyanopyridine
2-Cyanopyridine
At room temperature, 2-cyanopyridine has the appearance of a white to off-white solid and smells similar to almonds. Its molecular formula is C6H4N2 with a molecular weight of 104.11g/mol. Its IUPAC name is 2-cyanopyridine and is also known by the names such as Picolinonitrile, 100-70-9, Pyridine-2-carbonitrile, 2-pyridinecarbonitrile.
In addition to medicine it has applications in agrochemicals and fine chemicals. 2-Cyanopyridine is processed to produce chromium and zinc picolinate, which are then used in the diets of both humans and animals.
The chemical formula for 2-cyanopyridine is presented below:
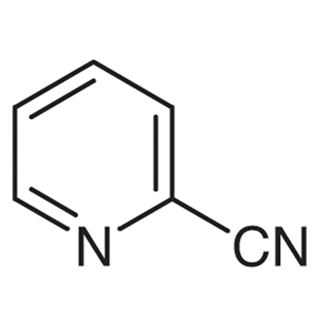
Uses
In the production of rimiterol hydrobromide, 2-cynopyridine is an important chemical step. Rimiterol hydrobromide is a bronchodilator. Additionally, it has a role as an intermediary step in the production of a variety of other compounds.
Additionally, it is utilized in the intermediate processes of the pharmaceutical, dye, and pigment industries. In the process of protein modification by amidation, it performs the role of a precursor to the corresponding amidate.
3-Cyanopyridine
Nicotinonitrile, also known as 3-cyanopyridine, is a kind of chemical compound that may be represented by the formula NCC5H4N. 3-Cyanopyridine is a white substance that is crystalline in appearance. It is also known by the names such as Nicotinonitrile, 100-54-9**, **3-pyridinecarbonitril and Pyridine-3-carbonitrile.
The chemical formula for 3-cyanopyridine is shown in the following diagram:
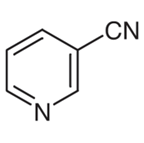
The structure of the molecule may be broken down into its component parts, which are a pyridine ring and a nitrile group connected to the 3-position.
2-chloropyridine has a melting point between 51-1240C (324 F0) and its boiling point is 206.9 degrees Celsius. The density of this compound is 1.1590 and its vapor pressure is 0.296 mm Hg.
It plays an important role in the production of niacinamide as well as niacin (Vitamin B3). Pymetrozine, 2-Chloro Nicotinic Acid, and 3-Aminomethylpyridine are some of the other important use areas for 3-Cyanopyridine. Other major application areas include agrochemicals and pharmaceuticals.
Synthesis
It is created through the ammoxidation of 3-methylpyridine and is a solid that has no colour:
H3CC5H4N + NH3 + 1.5 O2 → NCC5H4N + 3 H2O
Uses
- Nicotinonitrile is necessary in the production of niacin, which is a vitamin.
- Hydrolysis of 3-cyanopyridine that is catalyzed by nitrilase and carried out with Rhodococcus rhodochrous J1 strains that have been immobilized results in a quantifiable yield of nicotinamide (vitamin B3).
- Because additional hydrolysis of the amide to nicotinic acid is prevented by the enzyme, it is possible to carry out a synthesis that is more selective.
- In the production of medicines, the oxidation of 3-cyanopyridine with hydrogen peroxide results in the formation of 3-cyanopyridine N-oxide, which then hydrolyzes to produce nicotinic acid N-oxide.
- When hydrogen peroxide is used as the stoichiometric oxidant in the process of olefin epoxidation, the strong catalyst known as methyltrioxorhenium, or MTO, is activated. The performance of the catalytic reaction is greatly improved when heteroaromatic additives are present. Some examples of these types of heteroaromatic additives are pyrazole and 3-cyanopyridine. These Lewis base additives considerably stabilize reaction intermediates by coordinating to the rhenium core. Both the electronic and steric components of these additives play a key part in the process, and the impact of these additives cannot be overstated.
4-Cyanopyridine
At room temperature, 4-cyanopyridine takes on a white to off-white solid appearance. Its molecular formula is C6H4N2 with a molecular weight of 104.11g/mol. It is also known by the names such as Isonicotinonitrile, 100-48-1, 4-Pyridinecarbonitrile and Pyridine-4-carbonitrile.
The structural formula of 4-cyanopyridine is depicted in the following diagram:
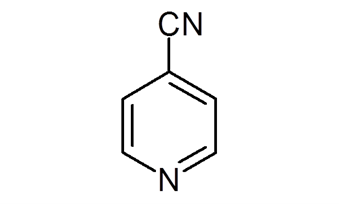
Uses
It plays an intermediary role in the production of chemical compounds as well as medicinal drugs. It is used in the production of the medication INH Isoniazid as well as a number of other medicines and agricultural chemicals.
Side effects
Cynopyridine is an irritant that induces depression of the central nervous system after consumption of half a cup or after inhalation at 6-12 ppm; it can cause harm to the liver and the kidneys and requires immediate medical attention.
Cynopyridine and its derivatives are known to irritate the skin, mucous membranes, and cornea when they come into contact with these tissues.
Safety
When working with cyanopyridine, it is important to use care. Workers have to be equipped with several pieces of personal protective equipment, the nature and extent of which depend on the potential for interaction. At a flow rate of 30 l/min for one hour, it was determined that a charcoal gas mask canister respirator was effective in protecting against a cyanopyridine concentration of 2 percent. Due to the fact that cyanopyridine and several of its derivatives are capable of penetrating rubber and plastic, gloves made of these materials cannot be depended upon to avoid skin contact.