Esters: Structure, synthesis and applications
Esters are formed from carboxylic acids. The ester group is formed when the hydrogen atom in the -COOH group of a carboxylic acid is exchanged for a hydrocarbon group. Any group that begins with an alkyl such as methyl or ethyl, or any group that begins with the benzene ring such as phenyl, is acceptable.
In the interaction between a carboxylic acid and an alcohol, at least one hydroxyl group (-OH) is replaced by a -O-alkyl (alkoxy) group, creating an ester. Glycerides, which are glycerol fatty acid esters, play a crucial role in living organisms. Fats and oils are the primary components of both animal and plant foods.
Esters can be found in pheromones and essential oils. Fragrances often consist of esters with low molecular weight. Because of their usefulness as solvents for a wide variety of plastics, plasticizers, resins, and lacquers, they are among the most widely used forms of synthetic lubricants. Due to the ester link between the monomers, polyesters can serve as functional plastics. Phosphoesters are responsible for DNA's structural integrity. Nitrate esters, such as nitroglycerin, are notorious for their explosive potential.
Structure
Esters are compounds with a double carbon-oxygen link and a further carbon-oxygen bond. Following this, an aryl or alkyl group is bonded to the oxygen atom. They are available in a wide range of sizes. Soybean oil is made of extremely long chain triglycerides, whereas very short chain fatty acids like allyl hexanoate give pineapples their distinctive aroma.
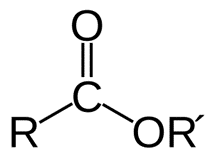
Esters of Carboxylic Acid
Low molecular weight carboxylic acid esters are colorless, odorless, and incommensurate with water liquids that have a high volatility. Many different chemicals contribute to the aroma and flavor of these meals. For example, bananas contain isopentyl acetate, wintergreen has methyl salicylate, and pineapples have ethyl butyrate. Synthetic flavors, perfumes, and cosmetics are all made with volatile esters like this, each with its own distinctive aroma.
Since lacquers, paints, and varnishes rely on the volatile esters ethyl acetate and butyl acetate as solvents, large quantities of these products are manufactured and sold. A wax is an ester of long-chain carboxylic acids and long-chain alcohols. Wax may be manufactured from a wide variety of plant and animal sources. Fats and oils are fatty acids, which are esters. They consist of glycerol and long-chain carboxylic acids.

Esters of Alcohols
Esters may also be produced by the reaction of alcohols with inorganic acids such as sulfuric, phosphoric, and nitric acid. Several nitrate esters, including nitroglycerin, are very flammable. The presence of phosphate esters in nucleic acids makes them significant in biology. The industrial applications are many as well. These include things like pesticides, fungicides, lubricant additives, and fuel and oil stabilizers.
Esters of Sulfuric Acid
Sulfuric acid esters and sulfuric acid are used in the production of colors and pharmaceuticals. Since it is the most prevalent ester of sulfuric acid, dimethyl sulphate is a potent toxin.
Synthesis of Esters
Esterification refers to the process by which an ester is produced as a byproduct of a chemical reaction. Esters have a sweet, fruity aroma and find widespread use in organic chemistry and biomaterials. This is why they have widespread application in the fragrance and flavor industry. Plenty of polymers also have ester linkages.
Esterification of alcohol and carboxylic acid
A carboxylic acid and an alcohol undergo Fischer esterification in the presence of a dehydrating agent. This technique has been around for quite some time, and it's been used to produce all sorts of things.
For typical esters like ethyl acetate, the equilibrium constant for such reactions is close to 5.
In the absence of a catalyst, the reaction proceeds at a snail's pace. It is common practice to employ sulfuric acid to hasten this process. Many additional acids, such as polymeric sulfonic acids, are also used. Since the process of esterification is very reversible, Le Chatelier's concept may be employed to produce more esters.
Dehydration of alcohol and carboxylic acid mixtures using catalysts is a well-established process. When working with moderate circumstances, the Steglich esterification process is a viable option for producing esters. Peptide substrates are very vulnerable to heat stress, hence this technique is often employed in peptide synthesis. The carboxylic acid is diluted with dicyclohexylcarbodiimide. The acyl-transfer catalyst utilized here is 4-dimethylaminopyridin.
Uses
Esters smell excellent just by taking a whiff for this reason they are utilized in a wide variety of applications, from flavoring food to creating fragrances like perfumes and colognes. They may be processed into polyester polymers, which in turn are utilized in the production of metal and plastic storage containers.
The following are some more applications of esters:
- Because of their pleasant aroma, esters find numerous applications in the fragrance and cosmetic industries.
- It's useful as a solvent for organic materials.
- Natural esters are found in pheromones.
- Natural fats and oils are the esters of glycerol and fatty acids.
- Nitrate esters, such as nitroglycerin, are commonly used in explosives.
- Fabrics made from polyesters may be spun into yarn.
- It is a key ingredient in both bar soap and liquid detergent because of its surfactant properties.
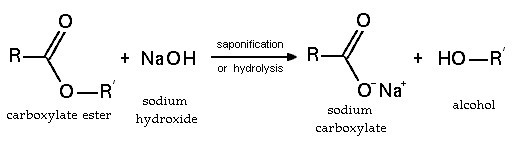
- Saponification is the process through which fats and oils are transformed into soap. This necessitates the presence of alkalies, such as sodium or potassium hydroxide, which hydrolyze esters (lye). Fires involving fats and oils can be extinguished using wet chemical extinguishers by employing the same saponification processes that render soap inflammable.