Iodobenzene: Synthesis, reactions, environmental exposure, safety and applications
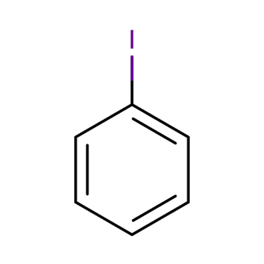
Iodobenzene is an organoiodine molecule that has one of its benzene rings switched out for an iodine atom. Iodobenzene has an empirical formula of C6H5I and a molecular weight of 204.01g/mol. In organic chemistry, it is utilised as an important intermediate in the synthesis process. It is a liquid that is combustible but has no colour; nevertheless, some older bottles may have a yellow appearance.
The chemical structure of Iodobenzene can be written as following:
Synthesis
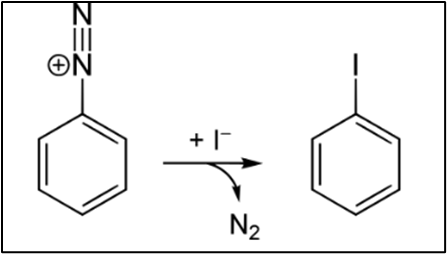
Iodobenzene may be obtained either by ordering it online or by performing the Diazotization Reaction with aniline in a chemistry lab. The amine functional group is initially diazotized by employing hydrochloric acid and sodium nitrite as the catalysts. Following this step, the phenyldiazonium chloride that was produced is treated with potassium iodide, which results in the production of nitrogen gas. To obtain a pure form of the substance, distillation with steam is performed.
Reactions
Iodobenzene is more reactive than bromobenzene or chlorobenzene because the connection between C and I is weaker than the link between C and either bromine or chlorine. Iodobenzene and magnesium are all that are required to manufacture Grignard reagent, also known as phenyl magnesium iodide. The phenyl anion synthon has a synthetic equivalent in the form of phenyl magnesium iodide, which functions in a manner analogous to that of the bromide analogue. Iodobenzene, when combined with chlorine, results in the formation of the complex Iodobenzene dichloride, which is a solid chloride that is dependable and unchanging.
Environmental Exposure
The release of iodobenzene into the environment can result from the use of iodobenzene as a reagent and the subsequent synthesis of it. This can happen via a variety of distinct waste streams. Iodobenzene has a vapour pressure of 1.06 mm Hg at 25 °C; as a result, if it were to be released into the air, it would only exist in the form of a vapour. Iodobenzene in the vapour phase of the atmosphere will degrade as a result of photochemically generated hydroxyl radicals catalyzing the process; the half-life for this reaction in air is estimated to be 15 days.
Safety
Get the person outside if they have breathed iodobenzene in. To give the patient artificial breathing if they are not breathing on their own. Please visit a doctor. If it gets on your skin, wash it well with soap and water. Please visit a doctor. If something gets in your eyes, you should rinse them well with lots of water for at least 15 minutes and then go to the doctor. If someone isn't responding, don't give them anything to eat or drink because they might swallow it. Use water to rinse your mouth. Please visit a doctor.
Use your gloves. Choose your personal protective equipment based on how much and how concentrated the dangerous material is.
There isn't a lot of consistency in the research about how people who work in manufacturing use contact lenses. Whether or not wearing contact lenses is good or bad depends on the shape of the material, the features and length of exposure, the use of additional eye protection devices, and how clean the lenses are. Still, some chemicals are so irritating or corrosive that it might be dangerous to wear contact lenses. If any of these things are true for you, it is best not to wear contact lenses. No matter what, it's still important to protect your eyes with normal things like goggles and a hat when you wear contact lenses.
Uses
Iodobenzene is beneficial in metal-catalyzed coupling processes such as the Sonogashira coupling and the Heck reaction, amongst others, when used as a substrate in these reactions. These reactions are facilitated by the oxidative addition of iodobenzene.
Iodobenzene is also useful as a substrate in metal-catalyzed coupling processes such as the Heck reaction and the Sonogashira coupling, amongst others. In the course of these reactions, the Iodobenzene passes through an oxidative addition.
Iodobenzene can be used as a starting material for the synthesis of biphenyl and stilbene. The Grignard reagent, a phenyl magnesium iodide that is essential in the process of organic synthesis, is the product of a reaction that this substance has with magnesium. It is possible to obtain solid chlorine from this substance once it has been mixed with chlorine to produce the complex Iodobenzene dichloride. During the Sonogashira reaction, this substrate is utilised in order to bring about the formation of a carbon-carbon bond between a terminal alkyne and an aryl halide.
Storage
Maintain the container in these conditions: it should be kept dry, cold, and airy. In order to avoid any accidental spilling once a container has been opened, it must be securely resealed and then placed in an upright position. Susceptible to change as a result of being exposed to light.