Methoxyphenol: Common isomers, synthesis and applications
Methoxyphenol is an organic molecule having a molecular formula C6H4(OH), and its molecular weight is 124.1372 g/mol. Methoxyphenol is a phenolic compound. It is composed of one oxygen atom with a methyl group attached (OCH3). This compound can either exist naturally or manufactured synthetically in a laboratory. This molecule, along with many of its derivatives, is a crucial intermediate in the production of a large number of other organic compounds, the majority of which have vital use in the food industry.
There are three basic isomeric forms of methoxyphenol which are as following:
- 2-Methoxyphenol
- 3-methoxyphenol
- 4-Methoxyphenol
All of these isomeric forms will be discussed in detail as following:
2-Methoxyphenol
The chemical formula for 2-methoxyphenol is C6H4(OH), and it is also known by the names such as o-methoxyphenol and 2-hydroxyanisole. This organic molecule occurs naturally and goes by the name guaiacol with a molecular weight 124.14 g/mol. It either exist in the form of crystals or a colorless to yellowish liquid. The production of this fragrant oil containing compound often involves the use of guaiacum, which is also known as wood creosote. This substance may be found, in addition to the essential oils of celery seeds, tobacco leaves, orange leaves, and lemon peels, in the actual seeds and leaves of these plants.
The chemical structure of 2-methoxyphenol can be written as:
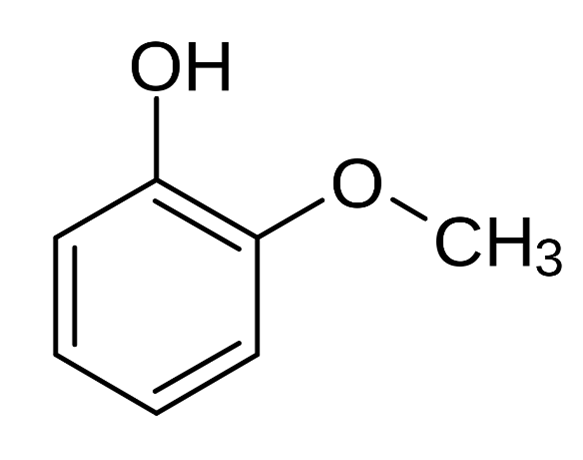
The boiling point of 2-methoxyphenol is 397.4 °F or even greater than that and its melting point is lower than -4 °F.
Synthesis
Potash and dimethyl sulphate, for example, can be used to catalyze the methylation of o-catechol, which ultimately produces 2-methoxyphenol as a byproduct. This can be done in the presence of o-catechol.
The products obtained from the reaction between C6H4(OH)2 and (CH3O)2SO2 are C6H4(OH)(OCH3) and HO(CH3O)SO2.
C6H4(OH)2 + (CH3O)2SO2 → C6H4(OH)(OCH3) + HO(CH3O)SO2
Fermentation of plant debris takes place inside the digestive system of the desert locust, Schistocerca gregaria, which results in the production of 2-methoxyphenol. This function is carried out by the bacteria known as Pantoea agglomerans, which may be found in the digestive system (Enterobacter). When locusts get together, this pheromone is a necessary component of the cocktail of pheromones that draws out the hordes.
Uses
2-methoxypenol has the following uses:
- In the field of chemistry, 2-methoxyphenol is an important component of many different compounds. Because of its origins in biomass, it may be considered a potential precursor to "green fuels."
- Two-methoxyphenol can be used as a starting material for the production of a number of other flavoring chemicals, including eugenol.
- Guaiacol is responsible for the production of around 85 percent of all vanillin. Through this process, mandelic acid is formed when glyoxylic acid is reacted with 2-methoxyphenol. Mandelic acid then undergoes oxidation, resulting in the production of phenylglyoxylic acid. In order to get vanillin, this acid has to go through a process called decarboxylation first.
- Antiseptic, local anaesthetic, and expectorant are only few of the functions that may be served by the medication known as two-methoxyphenol.
3-methoxyphenol
3-Methoxyphenol is regarded to be a part of the phenol family due to the fact that it is structurally similar to phenol but has a methoxy-substituent attached to the third position. It is a phenolilc compound belonging to the monomethoxybenzene class. The chemical formula for this substance is C7H8O2, and its molecular weight is 124.14 g/mol. It is a yellowish liquid that is clear at normal temperatures. A resorcinol serves as the basis for its construction.
The boiling point of 2-methoxyphenol is 244.0 °C and there are a few different species that naturally contain 3-methoxyphenol, such as Eriogonum brevicaule and Sedum crassularia.
The chemical formula of 3-methoxyphenol can be written as:
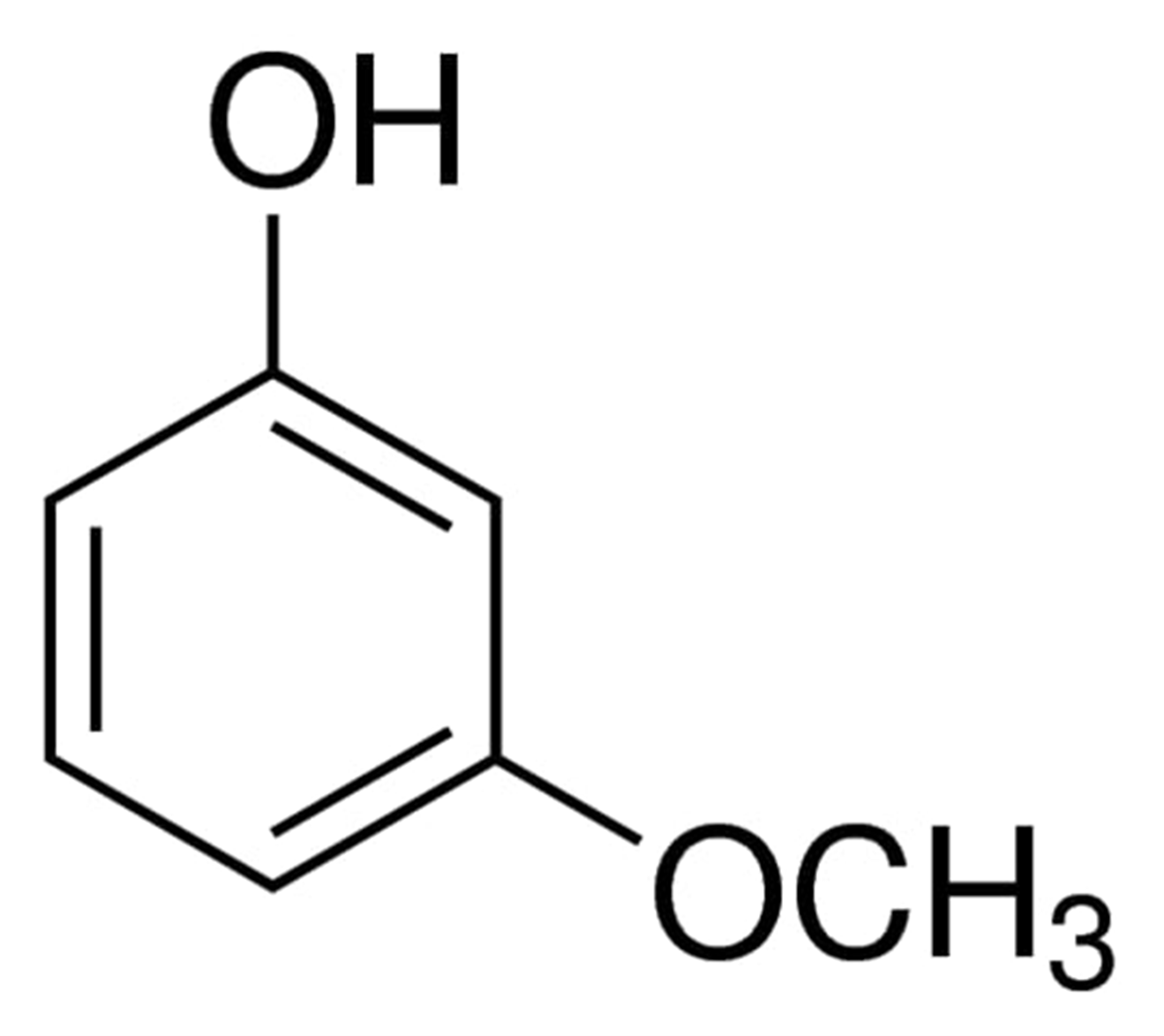
Uses
Using 3-methoxyphenol as an intermediate, the following compounds could be synthesized:
- Calixresorcinarene exhibiting symmetry of the C(4)
- 2-nitroso-5-methoxyphenol
- 6-methoxy-2(3H)-benzoxazolone
4-Methoxyphenol
Other names for 4-Methoxyphenol include MeHQ and Mequinol. It is a phenol that has use in both the field of dermatology and the field of organic chemistry.
To make this compound, an ethanolic solution is often used, and the mass percentage of tretinoin is typically set at 0.01%, while the concentration of mequinol is typically set at 2%. This drug is widely suggested by dermatologists as an effective treatment for the removal of liver spots. Patients diagnosed with diffuse idiopathic vitiligo have seen successful depigmentation after undergoing treatment with a Q-switched laser and lower than usual doses of mequinol.
The boiling point of 2-methoxyphenol is 475 °F and its melting point is 126.5 °F.
The chemical formula of 4-methoxyphenol can be written as:
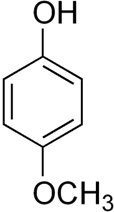
Synthesis
Through the process of a free radical reaction, it is possible to produce 4-methoxyphenol from p-benzoquinone and methanol. (4-Methoxyphenol)
Uses
The active ingredient in a lot of different skin depigmentation lotions is called 4-methoxyphenol. In the treatment of acne, it is common practice to combine the topical retinoids tretinoin and mequinol. Mequinol is a retinoid, and tretinoin also belong to this class of drugs.