Nitrophenol: Common isomers, synthesis and applications
Nitrophenol have the chemical formula HOC6H5(NO2) and its molecular weight is 139.110 g/mol. The conjugate bases of nitrophenol are also known as nitrophenolates. Nitrophenols have a higher acidity than phenol.
These compounds have a nitrophenol moiety, which is a benzene ring with hydroxyl and nitro groups linked to two of the ring's carbon atoms.
Nitrophenol is isomerized into three distinct forms which are as following:
- 2-Nitrophenol, also known as o-Nitrophenol.
- 3-Nitrophenol also known as m-Nitrophenol
- 4-Nitrophenol or p-Nitrophenol
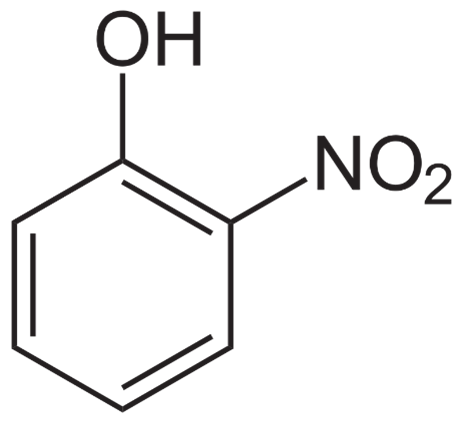
2-Nitrophenol
The ortho hydrogen of the hydroxyl group in 2-nitrophenol has been replaced with a nitro group. It has 139.11g/mol molecular weight. 2-nitrophenol is a solid with a bright yellow color. It is used as an indicator in a 2% alcohol solution with a pH range of 5.0-7.0 (colorless to yellow) Dye, paint coloring, rubber compounds, and fungicide production. The glucose reagent produces no significant color change and cannot be employed in carbon dioxide-containing environments.
The chemical structure of 2-Nitrophenol can be written as:
Synthesis
Nitrophenol may be produced in an autoclave by slowly (exothermically) heating 2-chloronitrobenzene in an 8.5% sodium hydroxide solution to 170 °C and holding that temperature and pressure for 8 hours. After the solution is generated, cooled, and acidified, a 95% yield is obtained.
Uses
It is used as an intermediate in the manufacture of a wide range of chemicals, including pigments and rubber, timber preservatives, photography chemicals, and fungal agents.
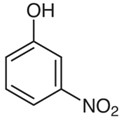
3-Nitrophenol
The hydrogen atom at the meta position to the hydroxyl group of phenol is substituted with a nitro group to produce 3-nitrophenol, which has a molecular formula C6H5NO3 and weight of 139.11g/mol. 3-nitrophenol is a colorless to light yellow crystalline compound. This absorbs into the liquid and is well blended in.
The chemical structure of 3-nitrophenol can be written as:
Uses
It is used as a pH indicator and fungicide on leather, leather surfaces, and leather products to inhibit the formation of mold, mildew, and dry rot fungus; also used in the synthesis of dyestuffs and other intermediates. On leather, leather surfaces, and leather items, this fungicide eliminates mold and mildew while also preventing dry rot and dry rot fungus.
Synthesis
3-nitroaniline is hydrolyzed by diazotizing it in aqueous sulfuric acid first, then gradually adding it to boiling dilute sulfuric acid. When the crude product cools, it solidifies and may be filtered out in 90% of situations.
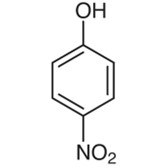
4-Nitrophenol
4-Nitrophenol has a nitro group instead of a hydroxyl group on the benzene ring, thus the alternate names p-nitrophenol and 4-hydroxynitrobenzene. 4 - Nitrophenol is a solid with a pleasantly sweet flavor that ranges in color from yellow to brown.
The chemical structure of 4-nitrophenol can be written as:
4-Nitrophenol, a member of the 4-nitrophenol family, is phenol with a nitro group substituting the hydroxyl group's para-hydrogen. This is a xenobiotic metabolite that is utilized by both humans and mice. This chemical is the acidic conjugate of a 4-nitrophenolate. 4-nitrophenol has a wide range of applications, including the production of colors, fungicides, insecticides, and even some pharmaceuticals.
In humans, acute (short-term) exposure to 4-nitrophenol by inhalation or ingestion can result in headaches, sleepiness, nausea, and cyanosis (blue color in lips, ears, and fingernails). It may be rather unpleasant to have anything brush against one's eyeballs. There is presently no evidence on the long-term consequences of 4-nitrophenol inhalation or oral intake in people or animals. There is currently no evidence that 4-nitrophenol has a deleterious impact on human reproduction, development, or cancer risk. The EPA does not consider 4-nitrophenol to be a probable carcinogen.
Dinitrophenols
HOC6H3(NO2)2 is the chemical formula for 2,4-dinitrophenol. It's a golden crystalline material that smells somewhat musty. Sublimes in the presence of steam and is soluble in a wide range of organic solvents and alkaline aqueous solutions. When it is dry, its explosiveness and potential for quick explosion are both quite high. It is biologically active and functions as a precursor to other chemicals. In mitochondrial-containing cells, it decouples oxidative phosphorylation from the electron transport chain. This is accomplished by allowing proton transport across the inner mitochondrial membrane and into the matrix.
Uses
DNP is one of the most efficient dinitrophenol herbicides. It is compatible with 2,4-Dinitro-o-cresol (DNOC), dinoseb, and dinoterb. It is utilized as a chemical link in the manufacturing chain to make sulphur dyes, wood preservatives, and picric acid. DNP can also be found in explosives and photography developing solutions.
Trinitrophenols
Picric acid, often known as phenol trinitrate, has the chemical formula C6H2OH (O2N3). However, due to the aromatic ring's sensitivity to electrophilic substitution processes, weak nitric acid cannot be utilized to nitrate phenol without first producing tars of extraordinarily high molecular weight. Anhydrous phenol is sulfonated using fuming sulfuric acid to reduce the possibility of unwanted reactions, and the resulting p-hydroxyphenylsulfonic acid is nitrated with strong nitric acid. As a byproduct, the process generates nitro groups and displaces the sulfonic acid group. Because the procedure is exothermic, it is critical that temperatures remain consistent. Picric acid can also be produced by directly nitrating 2,4-dinitrophenol with nitric acid.
Uses
By far the most major use has been the manufacture of firearms and explosives. Picric acid ammonium salts are known as Dunnite and Explosive D. Dunnite is more powerful than TNT, the most often used explosive, but it is also less stable.