Methoxypyridine: Common isomers, synthesis, applications and adverse reactions
Methoxypyridine is a colorless liquid with a molecular formulaC6H7NO and molecular weight 109.13 g/mol. There are three main isomers of 3 isomers of methoxypyridine which are as following:
- 2-methoxypyridine
- 3-methoxypyridine
- 4-methoxypyridine
These isomers can be discussed in detail as following:
2-Methoxypyridine
2-Methoxypyridine is a liquid that can range in color from colorless to light yellow and has an odor similar to that of fermented green tea. Some of the names that are used to refer to 2- methoxypyridine are 1628-89-3, Pyridine, 2-methoxy-,Methoxy-substituted pyridine and 2-methoxy-pyridine.
The structure of 2-methoxypyridine is represented by the chemical formula C6H7NO. And it is possible to determine that the molecular weight of 2-methoxypyridine is 109.13 g/mol by using its formula for the molecule.
The chemical composition of 2-methoxypyridine is depicted in the following diagram:
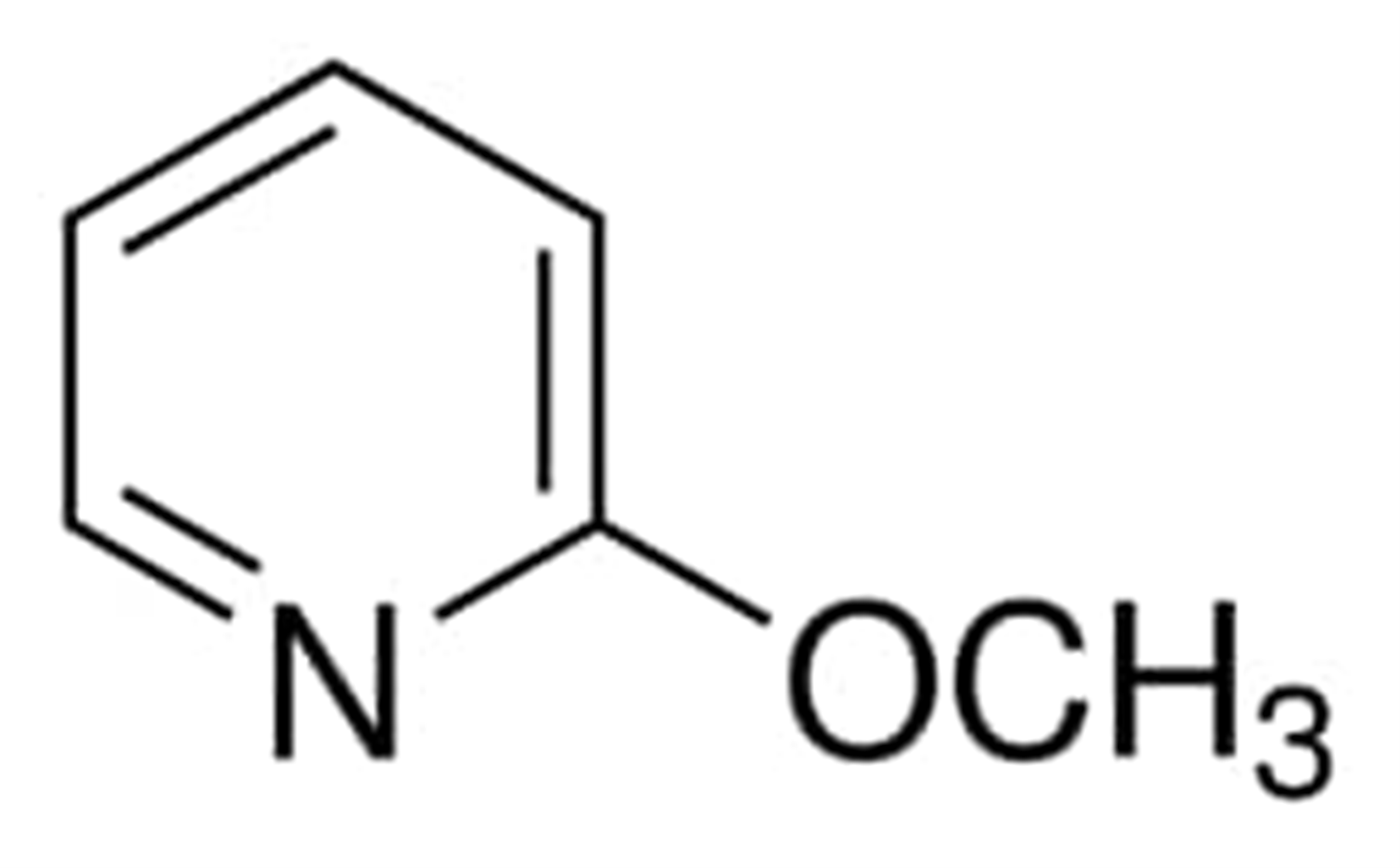
The temperature at which 2-methoxypyridine begins to boil is 142.0 degrees Celsius and the number assigned in the CAS registry for 2-methoxypyridine is 1628-89-3.
2- Methoxypyridine is so insoluble in water that it is almost impossible to dissolve it, however it may be dissolved in ethanol and it has density that falls somewhere in the range of 1.044 and 1.050.Thevalue given for the vapor pressure of 2-methoxypyridine is 2.58 [mmHg].
Uses
Its primary function is that of a flavoring agent.
Adverse reactions
- It is classified as one of the liquids and gases that have the potential to catch fire.
- It causes irritation to the skin and has the potential to lead to skin corrosion.
- It is highly irritating to the eyes and has the potential to cause substantial damage to the eyes if it is allowed to continue.
- Inflammation of the respiratory system is a distinct possibility. Even just one exposure is enough to irritate the respiratory tract and cause damage to certain organs that are the targets of the toxicity.
3-Methoxypyridine
3-Methoxypyridine is a liquid that can range in color from colorless to light yellow and has an odor similar to that of fermented green tea. Some of the names that are used to refer to 3-methoxypyridine are 7295-76-3, Pyridine, 3-methoxy-, Methoxy-substituted pyridine and 3-methoxy-pyridine.
The structure of 3-methoxypyridine is represented by the chemical formula C6H7NO and it is possible to determine that the molecular weight of 2-methoxypyridine is 109.13 g/mol by according to its molecular formula.
The chemical composition of 2-methoxypyridine is depicted in the following diagram:
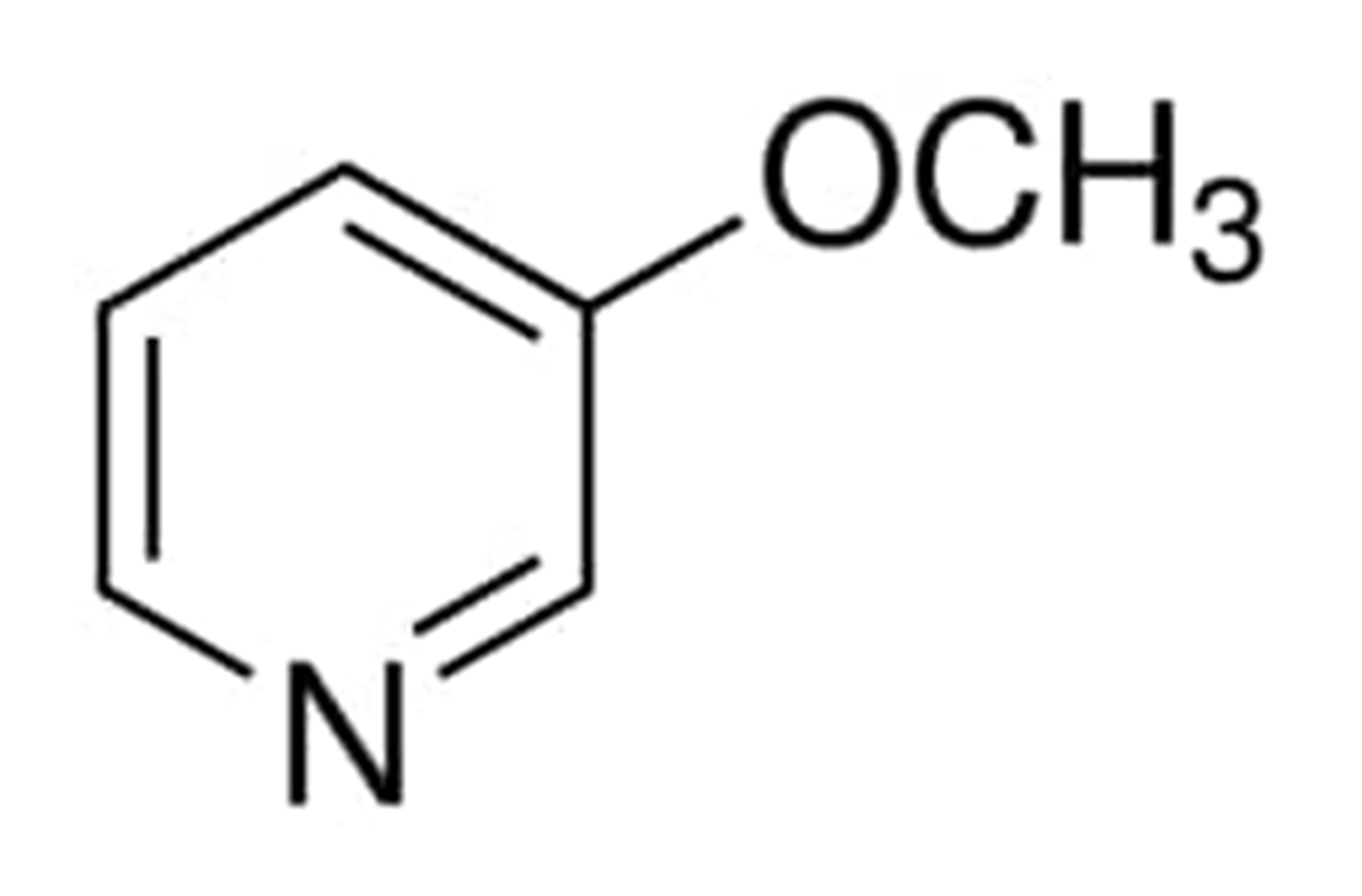
The temperature at which 3-methoxypyridine begins to boil is 65 degrees Celsius (15.0mmHg). The density of 3-methoxypyridine is determined to be 1.0830 grammes per millilitre and its vapor pressure has been determined to be 2.58 [mmHg].
3- Methoxypyridine is so insoluble in water that it is almost impossible to dissolve it, however it may be dissolved in ethanol.
3-Methoxypyridine is a derivative of the pyridine molecule that has an additional substituent. Flash photolysis with peroxodisulphate was used to analyze the oxidation kinetics of 3-methoxypyridine by sulphate radicals. This was done using peroxodisulphate. Through the process of ortholithiation, studies have been conducted on the 3-methoxypyridine substrate with mesityllithium serving as the metalating base.
Uses
Using 3-methoxypyridine as a catalyst makes it feasible to hasten the addition of certain 1,2-acyclic diones to activated acetylenic esters. This may be accomplished.
Adverse reactions
- This liquid and its vapor may catch fire.
- It causes skin irritation and may lead to skin corrosion.
- In addition to irritating the eyes, it has the potential to harm them permanently.
- The respiratory system may become inflamed. Even a single exposure can irritate the respiratory tract and be damaging to specific target organs.
4-Methoxypyridine
4-methylpyridine is a pyridine derivative with a molecular formula of C6H7NO and the molecular weight 109.13 grammes per mole. Some of the names that are used to refer to 4- methoxypyridine are 620-08-6, Pyridine, 4-methoxy-, methoxy-substituted pyridine and 4-methoxy-pyridine.
The chemical composition of 4-methoxypyridine is depicted in the following diagram:
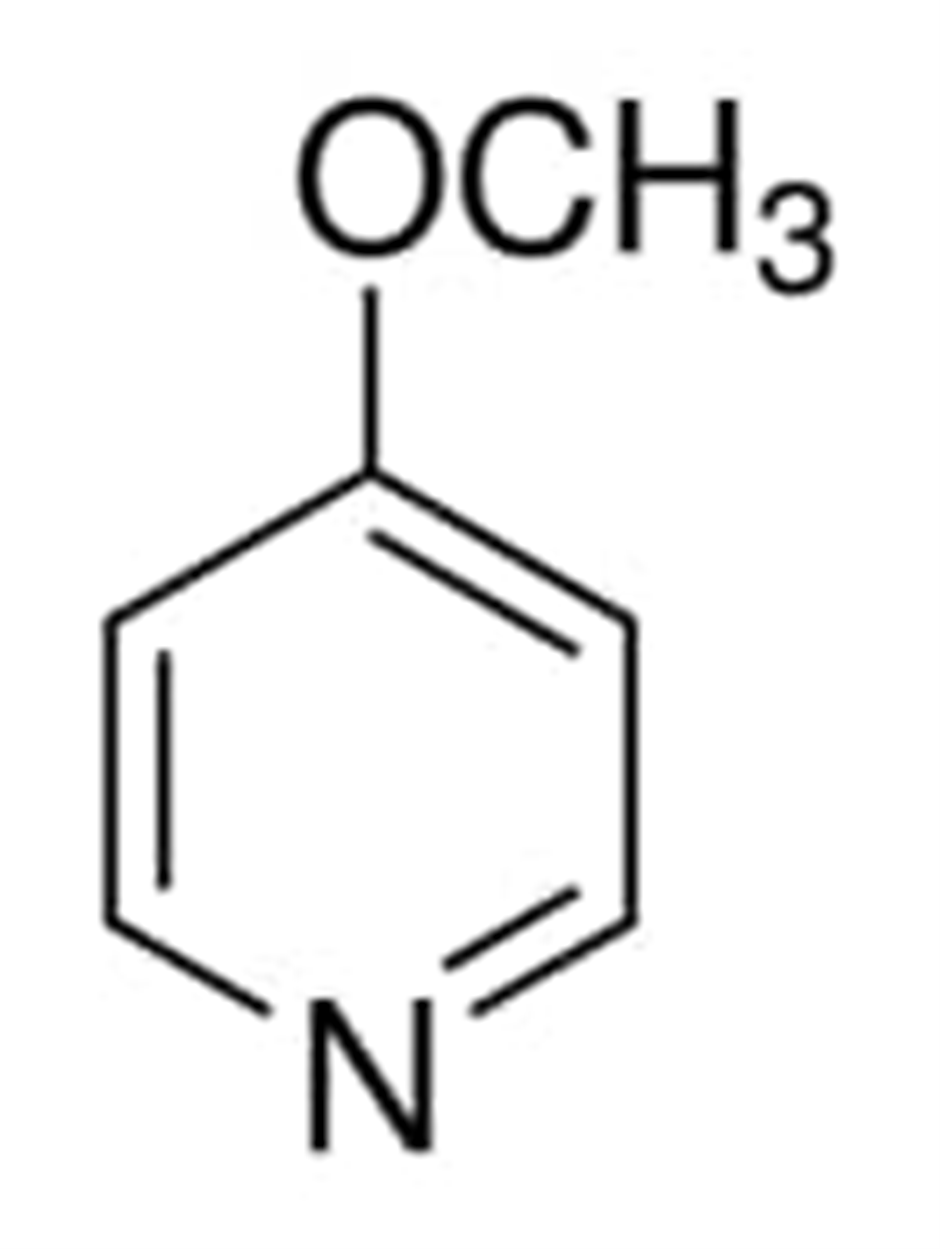
The temperature at which 3-methoxypyridine begins to boil ranges between 108-111 °C/65 mmHg (lit.) The density of 3-methoxypyridine falls between 1.075 g/mL at 25 °C (lit) and The number assigned in the CAS registry for 2-methoxypyridine is 1628-89-3.
It has been determined that 4 - methoxypyridine has a vapor pressure of 2.58 [mmHg] and it is so insoluble in water that it is almost impossible to dissolve it, however it may be dissolved in ethanol.
Synthesis
Catalytic hydrogenation was used to convert 4-methoxypyridine-N-oxide to 4-methoxypyridine. It is possible to synthesise 4-methoxypyridine using this 4-methoxypyridine starting material. Metalation investigations on 4-methoxypyridine have been conducted using mesityllithium as the metalating base.
Uses
During the process of the stereocontrolled synthesis of ()-pumiliotoxin C and ()-lasubine II, the starting reagent that was utilized was 4-methoxypyridine. Using this approach, it was also possible to effectively generate dihyropyridin-4-ones, which have the potential to act as ligands for nicotinic receptors. In order to accomplish this objective, this chemical was utilized.
Adverse reactions
- Flammable liquid and vapor.
- It makes the skin itch and could lead to skin corrosion.
- It irritates the eyes a lot and could do serious damage to the eyes.
- It could also cause inflammation in the respiratory system. Some of the organs it affects are hurt by it, and even a single exposure can make the respiratory tract irritated.