Nitros & Nitro Derivatives Available For Purchase
At Chempanda, we offer a range of nitros & nitro derivative chemical compounds that can be shipped to anywhere across the globe. We offer over 7660 different compounds that are available in varying purities and quantities.
Our Nitro Suppliers
We have partnered with a range of chemical manufacturers who specialize exclusively in synthesizing pyridines and their derivatives. With years of industry experience, our suppliers offer the most common pyridine compounds, or can custom manufacture pyridine compounds that you cannot purchase from most chemical suppliers.
With all orders, you can order the exact amount of chemical that you need - with no minimum order - in a cost and time effective manner that other suppliers cannot match.
Nitro Physical Properties & Structure
Organic chemical compounds that contain one or more nitro functional groups are referred to as ‘nitro’s’ or nitro compounds, as demonstrated by the formula RNO2, where the R group refers to an alkyl or aryl group.
Based on how the nitro group is attached to a carbon atom in the alkyl or aryl group determines the classification; primary, secondary or tertiary compound, with these different chemicals exhibiting different chemical properties and reactivities.
Nitro Derivatives
Nitro compounds commonly form as derivatives of hydrocarbons, where one or more hydrogens from these compounds are replaced by a nitro group. Both nitro derivatives can form as aromatic or aliphatic compounds (as described in the next section).
Nitro compounds can be formed into both amine and amide derivatives. Amides and amines can be formed via reduction reactions, with chemoselective derivatives with high yields.
The Reactivity of Nitros
In nitro functional groups, the central nitrogen atom is stabilized by resonance from the two attached oxygen atoms. This makes nitro functional groups strongly electron-withdrawing, and can also make the nitro group highly acidic.
If the R group of a nitro compound is an aromatic compound, electrophilic substitution is restricted, but nucleophilic substitution on the aromatic compound is possible with the right chemical conditions.
Aromatic nitro compounds can be synthesized by reacting nitric and sulfuric acid in the presence of an aromatic compound, whereas aliphatic nitro compounds can be synthesized in a wider range of reactions, including oxidation, decarboxylation and nucleophilic substitution.
Applications of Nitro & Derivatives
One of the most common applications of nitro-containing compounds is as explosives, such as 2,4,6-trinitrotoluene (TNT) or nitrocellulose, as well as different industrial propellants.
Nitro compounds are widely used, including in the manufacture of complex pharmaceutical compounds, and also in the manufacture of detergents and different dyes.
Because nitroalkanes can be readily converted into a wide range of different chemical compounds, they are often utilized as industrial synthons to synthesize other popular industrial chemical compounds.
Related Article(s)
Nitros: Synthesis, occurrence, reactions and applications Jul 28, 2022

Nitro compounds are those that have one or more nitro functional groups (NO2) in them. The nitro group is one of the most common and most often used examples of a functional group that gives a molecule explosive properties.
Nitroaniline: Common isomers, structure, synthesis and applicationsJul 4, 2022

Nitroaniline is a chemical compound made from aniline (C6H5NH2) with a nitro group added to it. Its chemical formula is H2NC6H4NO2 and is used to make medicines, cutting fluids and chemicals called benzotriazoles.
Nitrophenol: Common isomers, synthesis and applicationsJul 2, 2022
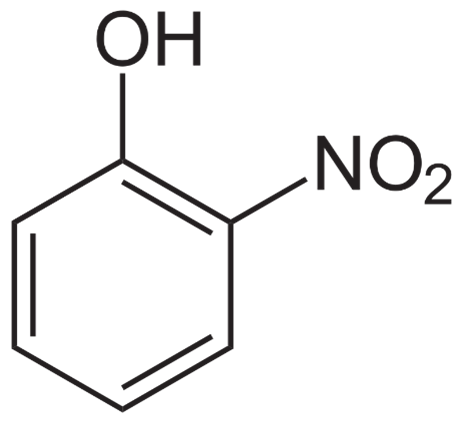
Nitrophenol has the chemical formula HOC6H5(NO2) and molecular weight of 139.110 g/mol. The conjugate bases of nitrophenol are also known as nitrophenolates. Nitrophenols have a higher acidity than phenol.
Nitrobenzoic acid: Common isomers, application and synthesisJun 30, 2022

Nitrobenzoic acid is ten times more acidic than the benzoic acid from which they originated. The production of nitrobenzoic acid results from the oxidation of styrene in boiling nitric acid. Nitrobenzoates are the salts and esters of nitrobenzoic acids.